陈晨副教授在Optics Express上发表论文
阅读次数: 发布时间:2021-11-22三维光子晶体禁带波长对结构/材料参数的依赖被广泛应用于化学和生物传感领域。相比反蛋白石结构的光子晶体,蛋白石结构由于体系中未被填充的空间较小,限制了液体折射率对光子晶体占空比的调制强度,因而传感灵敏度受到较大的限制。实验中我们观察到,除了禁带效应引起的反射以外,聚苯乙烯微球自组装形成的三维光子晶体加载不同折射率的液体后显示出巨大的透明度差异。进一步的计算研究表明,这一透明度变化的根源在于较厚光子晶体薄膜的非相干Fabry-Perot共振效应。在非标记传感性能表征的基础上,我们还将光子晶体薄膜用于艾滋病毒DNA扩增样品的荧光增强检测。实验结果表明,阴性和阳性样品加载的光子晶体不仅显示出透射光强度的差别,并且具有肉眼可分辨的荧光信号差异,这一研究结果对于多通道光子晶体传感器的研制具有重要的意义。
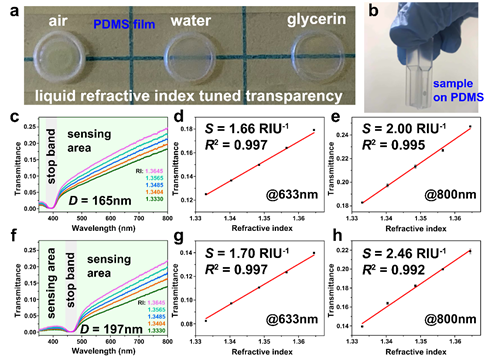
Fig.1 (a) Liquid RI enabled continuous transparency adjustment of the prepared PC dots. (b) PC sample on PDMS film attached to the inner wall of cuvette for spectra measurement. Dependence of transmission spectra on RI of potassium chloride water solution with sphere diameter of (c) 165 nm and (f) 197 nm. Dependence of transmittance at wavelength of 633 nm on RI with sphere diameter of (d) 165 nm and (g) 197 nm. Dependence of transmittance at wavelength of 800 nm on RI with sphere diameter of (e) 165 nm and (h) 197 nm. D, S, and RIU represent for diameter, sensitivity and refractive index unit, respectively.
相关工作以“Visible transparency tuning and corresponding sensing application of opal photonic crystals”为题发表在Optics Express上。公司物理系陈晨副教授为该文的第一作者兼通讯作者,上海交通大学医学院全球健康学院殷堃研究员为本文的共同通讯作者。该工作得到了国家自然科学基金项目的支持。
论文链接:
https://www.osapublishing.org/oe/fulltext.cfm?uri=oe-29-24-40419&id=464958
